What is the Department of Pediatric Urology and What Diseases Does It Cover?
The Department of Pediatric Urology is a medical discipline that deals with the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of diseases related to the urinary tract and reproductive organs of children from birth to adolescence. This department specializes in the treatment of congenital or acquired abnormalities in the kidneys, bladder, ureters, urethra and genital organs. The Department of Pediatric Urology offers a comprehensive service that includes both surgical and non-surgical treatment methods.
About the Department of Pediatric Urology
The pediatric urology department is a medical branch that provides services for the evaluation and treatment of diseases related to the urinary tract and genital organs of children. In this department, age-appropriate treatment approaches are determined by taking into account the physiological and psychological development processes of children. The pediatric urology department specializes in treating urological problems that can be seen in both boys and girls and supports the healthy growth of children by guiding families.
Who is a Pediatric Urologist and What Are Their Duties?
A pediatric urologist is a surgeon who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases of the urinary tract (kidneys, ureters, bladder) and genital organs of children. These specialists have extensive experience and qualifications in evaluating and managing children's urologic problems.
The main duties of the pediatric urologist are:- Evaluation and Management of Urinary Tract Obstruction (Hydronephrosis): Monitoring and treatment of kidney enlargement (hydronephrosis) due to congenital or acquired obstruction of the urinary tract in children.
- Evaluation and Management of Urinary Disorders: Evaluation and treatment of urinary problems (e.g., bedwetting, frequent urination) in children.
- Vesicoureteral Reflux and Urinary Tract Infections Requiring Surgery: Evaluation and surgical treatment of vesicoureteral reflux, which is the backward flow of urine from the bladder to the kidneys.
- Surgical Repair of Urinary System and Genital Anomalies: Surgical correction of genital anomalies such as hypospadias and disorders of sex development.
- Surgery for Groin Area Diseases: Surgical treatment of groin area diseases seen in childhood and adolescence, such as undescended testicles, hydrocele/hernia and varicocele.
- Evaluation and Surgical Management of Kidney Stone Disease: Evaluation of kidney stones in children and performing necessary surgical interventions.
- Surgical Management of Kidney, Bladder and Testicular Tumors: Surgical treatment of tumors and cancers in the kidney, bladder and testicles.
- Evaluation and Management of Urinary System Problems Diagnosed Before Birth: Postnatal evaluation and treatment of urinary system problems diagnosed before birth.
- Management of Urinary Tract Problems Associated with Neurological Conditions: Evaluation and management of urinary tract problems associated with neurological conditions such as spina bifida.
What Diseases Does Pediatric Urology Cover?
The pediatric urology department covers many different diseases affecting the urinary tract and genital organs.
These diseases include:- Urinary Obstruction (Hydronephrosis): Enlargement of the kidneys with urine in children. It is a disease that usually does not require follow-up, but in some cases requires surgery.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTI): A common condition in children and usually requires antibiotic treatment.
- Kidney Stones: Stones formed in the kidneys can cause pain and urinary tract obstruction.
- Hypospadias: In boys, this is a condition in which the urinary meatus is located in a different location than normal and may require surgical intervention.
- Undescended Testicles: This is a condition in which the testicles do not descend into the scrotum in male infants and is usually corrected with surgical treatment.
- Bladder Reflux (Vesicoureteral Reflux): This is the condition in which urine leaks back from the bladder to the kidneys, which can cause damage to the kidneys.
- Bedwetting (Nocturna Enuresis): This condition, which is frequently seen in children, is not usually a sign of a health problem but may require treatment.
- Genital Anomalies: Congenital or acquired abnormalities of the genital organs.
What are Pediatric Urology Examinations?
Pediatric urology examinations include various evaluations to accurately identify urological problems in children and create a treatment plan.
These examinations typically include:- Physical Examination: Manual examination of the genitals and urinary tract to assess the child's overall urological health.
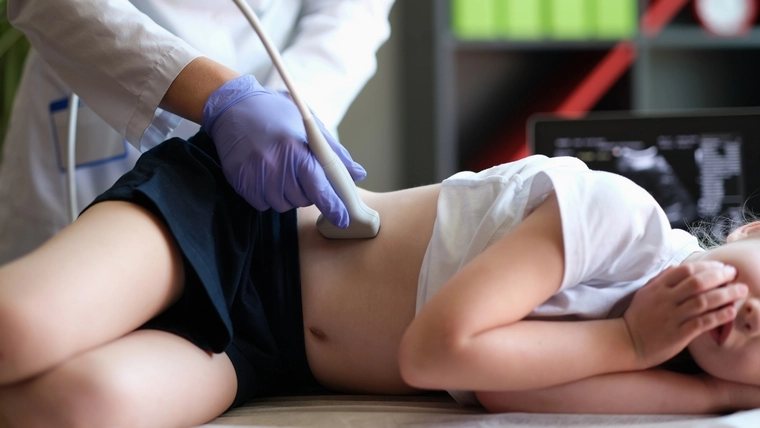
- Ultrasonography: A common imaging method used to obtain detailed images of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and genitals. This helps identify kidney stones, tumors, or other structural abnormalities.
- Voiding Cystourethrography (VCUG): An x-ray imaging test that involves injecting contrast material into the bladder to detect conditions such as bladder reflux.
- Doppler ultrasound: A special type of ultrasound used to evaluate blood flow in the testicles and other genital organs, useful in detecting conditions such as varicoceles or torsion.
- Urine Tests: Examination of urine samples in a laboratory environment to detect infections or other abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Evaluation of kidney function and general health status.
- Nuclear Medicine Tests: Special tests used to evaluate kidney function and urine flow.
- Urodynamic Tests: Tests that evaluate urine flow, bladder function, and the voiding process.
These examinations provide the pediatric urologist with comprehensive information about the child's urological health, helping him or her create an accurate diagnosis and an effective treatment plan.
What Methods Are Used in Pediatric Urology Treatments?
Pediatric urology treatments may include surgical and non-surgical methods, depending on the type and severity of the disease.
Commonly used treatment methods:- Medication: Antibiotics, painkillers, and other medications for conditions such as urinary tract infections.
- Surgical Intervention: Surgical operations to correct conditions such as hypospadias, undescended testicles, kidney stones.
- Behavioral Treatments: Behavioral treatment methods used in situations such as bedwetting.
- Physiotherapy: Exercises used to improve bladder functions.
- Diet and Lifestyle Changes: Recommended changes to prevent kidney stones and maintain urinary tract health.
When Should You Go to the Pediatric Urology Department?
If your child has symptoms such as pain during urination, incontinence, frequent urination, bedwetting, abnormalities in the genital area, or changes in urine color, you should consult the pediatric urology department. In addition, if there are congenital urological problems or genetic risk factors such as kidney disease in the family, regular consultation should be received from this department.
What is Done During a Pediatric Urology Examination?
During a pediatric urology examination, the specialist doctor first listens to the child's complaints and medical history. A physical examination is performed and, if necessary, the tests mentioned above are applied. During the examination, the doctor and the family work together to ensure that the child is relaxed and does not experience stress. A diagnosis is made and a treatment plan is determined according to the examination results. The family is given detailed information about this plan and, if necessary, surgical or non-surgical treatment methods are applied.


