What is the Intensive Care Unit? What are the Conditions that Require Treatment in the Intensive Care Unit?
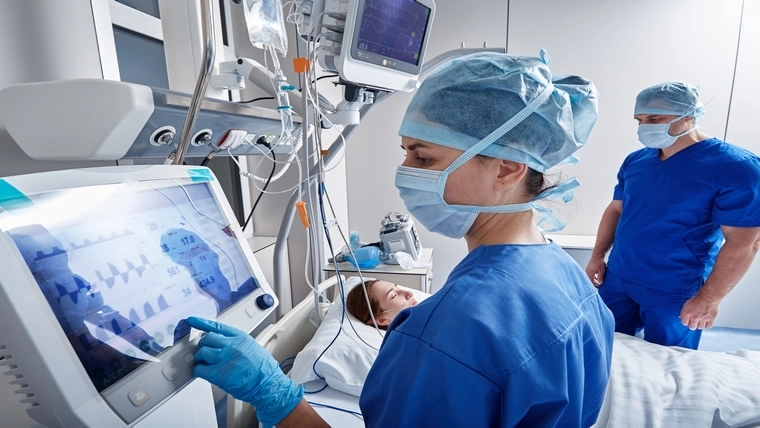
The Intensive Care Unit is a specialized hospital unit where patients with life-threatening conditions are closely monitored and treated 24 hours a day. This unit is designed to support the vital functions of critically ill patients and ensure their recovery.
About the Intensive Care Unit
Intensive care units are one of the most complex and technologically advanced areas of modern medicine. These units are specially equipped for continuous monitoring and treatment of critically ill patients. The advanced technological devices and trained medical staff used in the intensive care unit play a major role in the recovery process of patients.
In intensive care units, patients' vital signs are continuously monitored. This monitoring includes parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature.
Who is a General Intensive Care Specialist and What Are Their Duties?
A general intensivist is a specially trained physician who is responsible for the diagnosis, treatment, and care of critically ill patients. These specialists usually complete a residency in one of the primary medical specialties, such as anesthesiology, internal medicine, or surgery, followed by additional training in critical care medicine.
The main duties of the intensive care specialist are:- Managing the diagnosis and treatment of critically ill patients
- Managing life support systems
- Coordinating the multidisciplinary team
- Communicating with patients and their relatives
- Managing ethical decision-making processes
Scientific studies show that general intensive care specialists accelerate the recovery process of patients and reduce complication rates.
What are the conditions that require treatment in the Intensive Care Unit?
Conditions requiring treatment in the intensive care unit are usually life-threatening and require constant monitoring.
These situations include:- Acute Respiratory Failure: A condition in which the body cannot take in enough oxygen or remove carbon dioxide. This can be due to various reasons. Patients usually require mechanical ventilation support.
- Septic Shock: A life-threatening condition resulting from the body's overreaction to infection. Characterized by a drop in blood pressure, impaired organ function, and widespread inflammation. Requires intensive antibiotic therapy, fluid replacement, and sometimes vasopressor medications.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: It includes serious problems related to the heart and vascular system such as heart attack, heart failure, arrhythmias. These patients require continuous cardiac monitoring, drug therapy and sometimes emergency intervention.
- Neurological Emergencies: Includes emergencies related to the brain and nervous system, such as cerebral hemorrhage, stroke, status epilepticus. These patients require continuous evaluation of their neurological status and specific treatments.
- Multiple Organ Failure: The condition in which more than one organ fails to perform its functions. It is usually seen after serious trauma. Intensive supportive treatment and management of each organ's functions separately are required.
- Serious trauma and injuries: This includes serious injuries resulting from traffic accidents, falls, or other accidents. These patients often suffer multisystem damage and require surgery, blood transfusions, and intensive care support.
- Heart attack and other cardiac events: These include myocardial infarction (heart attack), unstable angina, serious arrhythmias, etc. These patients require emergency cardiac care, medication, and sometimes angioplasty or bypass surgery.
- Cerebral hemorrhage and other neurological emergencies: Includes intracranial hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, severe head trauma, etc. These patients require neurosurgical intervention, intracranial pressure monitoring, and intensive neurological care.
What is the Importance of Intensive Care Units?
Intensive care units provide a critical medical service that increases patients’ chances of survival and accelerates the recovery process. The importance of these units can be summarized in the following points:
- Saving Lives: Intensive care units play a crucial role in saving the lives of critically ill patients. These units provide continuous 24-hour monitoring of patients whose vital functions are seriously impaired and provide the necessary interventions quickly.
- Use of Advanced Technology: Intensive care units contain the latest medical technologies. Advanced devices such as mechanical ventilators, patient monitors, and dialysis machines support patients' vital functions and accelerate the healing process. Thanks to these technologies, patients' conditions can be monitored continuously and precisely.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Intensive care units are places where physicians, nurses and other healthcare personnel from different areas of expertise work together. This multidisciplinary approach allows complex cases to be managed more effectively.
- Patient Safety: Intensive care units are designed to provide the highest level of patient safety. Protocols such as infection control, medication safety, and fall prevention are meticulously implemented. In patients who are kept under constant observation, possible complications can be detected early and intervened.
- Management of Critical Situations: Intensive care units are specialized units for the management of suddenly developing critical situations. For example, in the event of a cardiac arrest in a patient, the intensive care team can intervene quickly. Special equipment and trained personnel in these units ensure that critical situations are managed effectively.











