What is a Diabetes Center?
Diabetes Centers are health institutions that provide services with a multidisciplinary approach, carrying out the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up processes of diabetic patients. These centers aim to increase the quality of life of patients by providing all the medical services required for the management of diabetes. Diabetes centers provide an environment where many health professionals such as specialist doctors, nurses, dietitians, psychologists and educators work together.
About Diabetes Center
Diabetes centers provide specialized services for the needs of diabetic patients. In these centers, personalized treatment plans are created according to the individual needs of patients. Diabetes centers help patients control their blood sugar levels, prevent complications of diabetes, and maintain the overall health of patients. They also provide education and support to help patients learn to live with diabetes.
What is done in the Diabetes Center?
Diabetes centers provide basic services such as diagnosing patients with diabetes, planning the treatment process, and performing regular check-ups. Important parameters such as blood sugar levels, kidney functions, and eye health are regularly monitored. In addition, necessary precautions are taken to prevent and manage complications related to diabetes. Patients are also informed about issues such as creating nutrition plans, exercise recommendations, and psychological support.
What are the procedures and tests performed at the Diabetes Center?
In diabetes centers, a series of procedures and tests are performed for the diagnosis, follow-up and management of diabetes. These procedures and tests are performed to closely monitor the health status of diabetic patients and prevent possible complications.
Here are some important procedures and examinations commonly performed in diabetes centers:- Blood Glucose Tests: Blood glucose tests are a basic part of diabetes management and are performed regularly to determine whether patients' blood sugar levels are under control. Blood glucose testing is usually performed by taking a blood sample from a fingertip.
- HbA1c Test: This test shows your average blood sugar level over the last 2-3 months. The HbA1c test plays a critical role in diabetes management and is used to evaluate the effectiveness of your treatment plan.
- Urine Tests: Urine tests are performed to evaluate the effects of diabetes on the kidneys and detect substances such as protein or albumin. These tests are used to early diagnose kidney complications such as diabetic nephropathy.
- Kidney Function Tests: Tests such as blood creatinine and BUN (blood urea nitrogen) are done to evaluate the functionality of the kidneys. These tests are important for maintaining kidney health and preventing possible kidney failure.
- Eye Exams: Regular eye exams are performed to evaluate the effects of diabetes on the eyes. Diabetic eye diseases such as retinopathy, cataracts and glaucoma are diagnosed and treated early.
- Foot Health Assessment: Regular foot examinations are performed to check for foot wounds and infections, which are common in diabetic patients. Foot health assessment is critical for preventing and treating potential complications.
- Cardiovascular Tests: Since diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, cardiovascular tests such as ECG, stress test and blood lipid profile are performed regularly. These tests are vital for maintaining heart health.
- Insulin Therapy and Education: In diabetes centers, patients are given insulin therapy and education on the proper use of insulin. In addition, patients are informed about the use of devices such as insulin pumps.
- Nutrition and Diet Counseling: Dietitians create a suitable nutrition plan for patients to manage diabetes. This plan helps keep blood sugar under control and improves the quality of life of patients.
What are the diseases treated at the Diabetes Center?
Diabetes centers provide diagnosis, treatment and management of various diseases that are directly caused by or related to diabetes. Diseases treated in these centers can generally be classified as complications of diabetes or conditions that occur together with diabetes.
Here are some of the diseases commonly treated at diabetes centers:- Type 1 Diabetes: A type of diabetes characterized by insulin deficiency that develops as a result of the immune system attacking the pancreatic cells. Treatment is usually managed with insulin therapy and close blood sugar monitoring.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A type of diabetes in which the body's cells develop resistance to insulin and insulin production is inadequate. Treatment is through lifestyle changes, oral medications, and insulin when necessary.
- Gestational Diabetes: A type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after birth. During pregnancy, blood sugar levels must be carefully monitored and managed for the health of the mother and baby.
- Prediabetes: A condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Prediabetes increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and is important to manage with early intervention.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: It is a complication of diabetes that can damage the blood vessels in the eyes in the long term and lead to blindness. Diabetes centers offer regular eye examinations and treatment options.
- Diabetic Nephropathy: A complication of diabetes that causes damage to the kidneys and can lead to kidney failure. Treatment includes monitoring kidney function and measures to prevent kidney damage.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: This condition, known as nerve damage, occurs as a result of long-term damage to nerves caused by diabetes. It manifests itself with symptoms such as numbness, tingling and pain in the hands and feet.
- Diabetic Foot Wounds: Wounds that occur on the feet as a result of diabetic neuropathy and vascular diseases can lead to serious infections and amputation if left untreated. Special care services are provided in diabetes centers for the prevention and treatment of such wounds.
- Diabetes-Related Cardiovascular Diseases: Diabetes is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease, hypertension, and stroke. Prevention and management of these diseases are part of the treatment plans offered at diabetes centers.
- Obesity: Obesity is a significant risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. In diabetes centers, nutrition and exercise programs and behavioral therapies are applied for weight management and obesity treatment.
Diabetes centers aim to minimize patients' diabetes-related complications and improve their quality of life by adopting a multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis, treatment and management of these diseases.
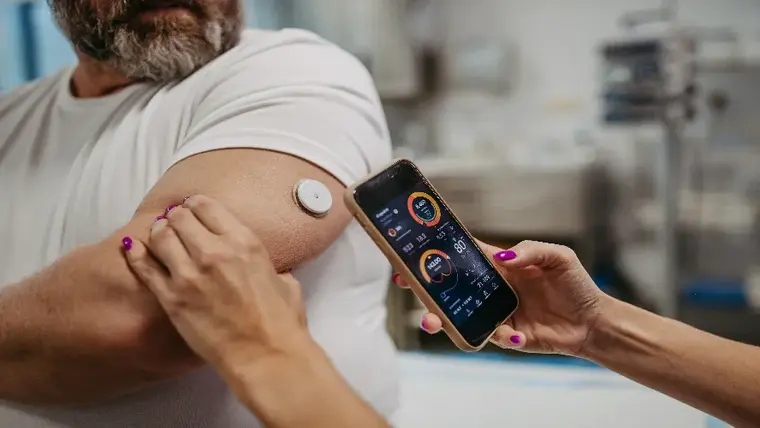
What are the Health Technologies (Devices) Used in the Diabetes Center?
In diabetes centers, patients' health status is closely monitored using modern medical devices and technologies. Blood sugar meters, continuous glucose measurement systems, insulin pumps, HbA1c analyzers and retinal scanning devices are among the technologies commonly used in these centers. These devices help patients manage their diabetes more effectively.
When Should You Contact a Diabetes Center?
If you have symptoms of diabetes or have been diagnosed with diabetes, it is important to visit a diabetes center. Also, if you want to optimize your current diabetes treatment and have regular checkups to prevent or manage diabetes-related complications, a diabetes center will provide you with the most appropriate treatment plan. Diabetes centers play a vital role, especially for patients who have difficulty controlling their blood sugar, need insulin therapy, or have difficulty coping with complications caused by diabetes.




